Mooring Ropes are primarily used to secure a boat to its berth against the effects of wind and current or other forces. When most ships are berthing, they are tied to the bollards on the shore with cables, so the mooring ropes play an important role in mooring. When mooring, the specific use of mooring ropes should be determined according to the quay condition, ship length, rope strength, mooring time length, weather and tide condition.

Function of the mooring ropes
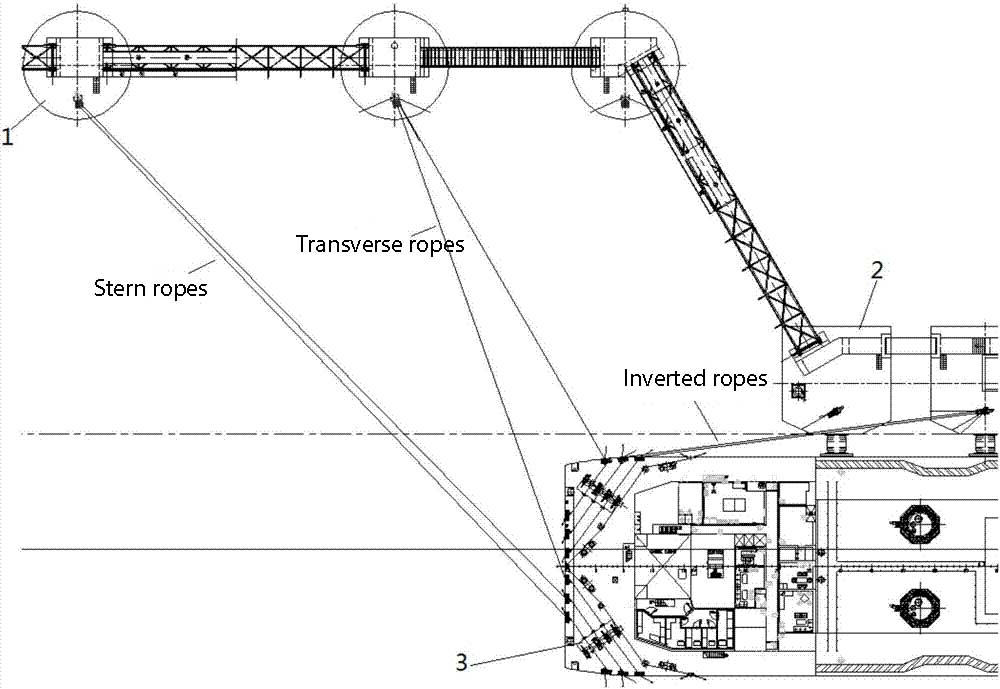
Mooring arrangements include the following types of ropes:
- Transverse ropes are mooring ropes extending from the bow and stern decks of the ship, close to the direction perpendicular to the fenders, and are used to limit the lateral movement of the ship away from the berth.
- Inverted ropes are mooring ropes deployed from the ship’s main deck (or sometimes from the bow/transom deck), close to parallel to the direction of the bumper, and are used to limit the ship’s longitudinal movement along the direction of the bumper.
- Head and stern ropes are sometimes also provided, these cables provide an intermediate function between cross and spool cables. They are usually not required for most installations, however they provide the required function in high currents and/or swells or currents pushing the bow or stern off the fender.
Length of mooring ropes
For ships berthed at berths, the optimal mooring rope lengths for deployment should be between 35m and 50m, and the same lengths should be equal to ensure that the forces on the lines are evenly distributed.
Optimum mooring rope angle
In order to maximize the carrying capacity of the mooring ropes, and minimize the need for line adjustments to accommodate tidal and draft changes, the following points should be considered:
- The vertical angle of the mooring ropes should be kept below 25 degrees from the horizontal as far as possible.
- The mooring structure of the transverse lines should be kept at a sufficient distance from the direction of the fenders to limit the vertical angle of the mooring lines at all tides and ship drought conditions. The same is true for the mooring structure of the tumbled line. Generally, a smaller vertical angle results in less tension on the mooring lines and reduces lateral loads on the berth mooring structure.
- Longer ropes will result in reduced stiffness and may be counterproductive to keeping the vessel’s manifold within the safe working range of the boom or hose.
Therefore, berth design should strike a careful balance between several conflicting mooring rope properties and requirements to achieve an optimal berth design.
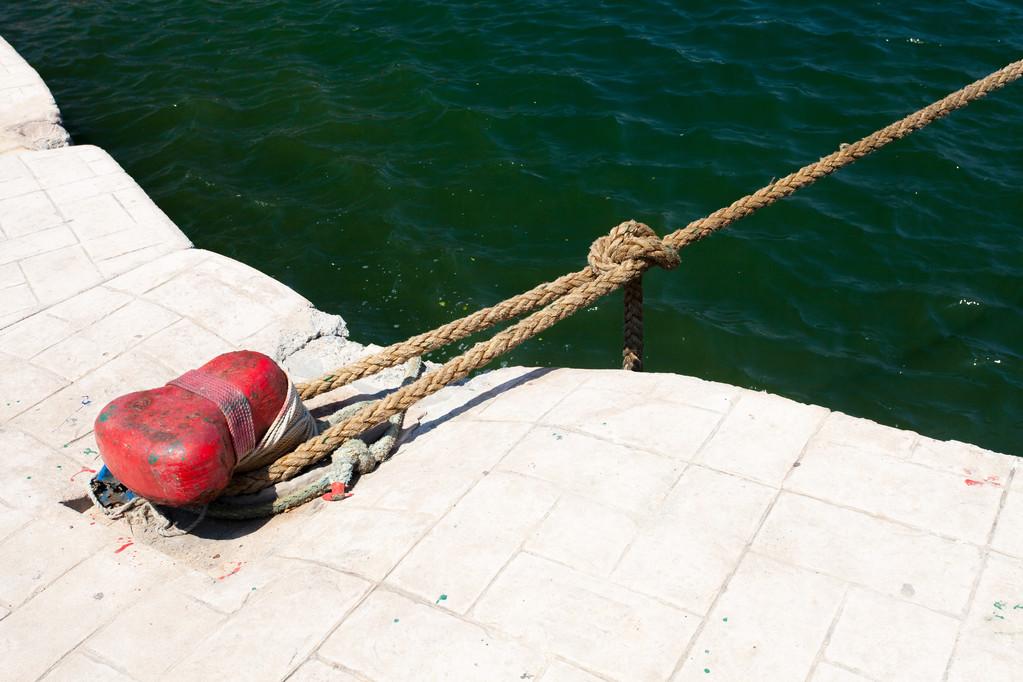

Stiffness of mooring ropes
The same material should be used for all mooring ropes and stern ropes of the same function (i.e. drop lines, cross lines, etc.), and the berth mooring structure is positioned so that the lengths of the mooring lines are approximately the same. This prevents mooring loads from concentrating on the shorter (harder) lines, resulting in a safer mooring structure. Cables that are parallel to each other shall, to the extent possible, be of the same material and length.
Berth designers should be aware that different types of ropes may be fitted within the range of vessels accepted by the berth, namely traditional fibre ropes, HMSF ropes and steel wire ropes. All possible rope types should be considered in berth design.
Mooring ropes operation
Minimize manual manipulation of mooring ropes at the berth where possible. It is recommended to provide winches or roller fairleads to operate mooring ropes for larger vessels. The winch can be self-contained or installed as part of the quick-release hook.
Anti-friction protection of mooring ropes
Protection of the mooring ropes should be provided to ensure safe passage of the lines and avoid potential damage to the ship’s mooring ropes from sharp edges on structural components including steel girders and concrete. Countersunk head bolts should be used on all quick-release hooks and bollards to prevent damage to the mooring ropes. Bolts and nuts should be epoxy coated to prevent ropes contact and protect bolts from corrosion.

Rebound risk of mooring ropes
When designing shore mooring facilities, the same design factors as ship installations should be considered to avoid possible injury to personnel when cables fail under tension.
Summary
In fact, the dangerous situation of ship mooring rope falling off and breaking occurs from time to time, which has a great impact on ship safety and port production. Therefore, the rational use of mooring ropes helps greatly reduce the accident risk of ships in mooring engineering. If you still have questions about the proper use of mooring ropes, please do not hesitate to contact us. Boomarine is a professional marine equipment supplier, we will recommend tailor-made solutions for you according to your actual situation.








